Zerojudge第四屆簡單的小競賽題解
[簽到] (Zerojudge_f026 不公開)
題目:輸出鬜衟。
解法:輸出。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "鬜衟\n";
}
1. Say HELLO! (Zerojudge_e412 練習題)
題目:輸出 $\text{HELLO,} +$ 字串。
解法:要讀取整行。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
while (getline (cin, str))
cout << "HELLO," << str << '\n';
}
2. Coder King (Zerojudge_f941)
題目:求一數列 (只有 $1, 2, 3$) 的非嚴格遞增 $\text{LIS}$。
解法:不要用 $O(n\times log(n))$,可以直接用 $a[3]$ 存目前最大值,再去比對,$O(n)$ 就能完成。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <stdio.h>
#define gu() getchar_unlocked()
#define big(X,Y) (X>Y?X:Y)
int main() {
int a[4] = {0};
char c = gu();
while (c >= '1' && c <= '3') {
if (c == '1')
a[1]++;
else if (c == '2')
a[2] = big (a[1], a[2]) + 1;
else
a[0] = big (a[1], a[2]), a[3] = big (a[0], a[3]) + 1;
c = gu();
}
a[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
if (a[i] > a[0])
a[0] = a[i];
printf ("%d\n", a[0]);
}
3. WandaVision轉圈圈 (Zerojudge_f971)
題目:輸出 $1$ 的 $n$ 次方根。
解法:$0≤ k <n$,$x_k = cos( k\times 2π/n ) + sin( k\times 2π/n ) i$。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
const LD pi = acos (-1);
int n;
void out (LD x) {
if (-0.0005 < x && x <= 0) {
cout << "0.000";
return;
}
bool lit = 0;
if (x < 0)
lit = 1, x = -x, cout << '-';
cout << fixed << setprecision (3) << x;
}
void solve() {
pair<LD, LD> p[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p[i].first = cos (2 * i * pi / n);
p[i].second = sin (2 * i * pi / n);
}
sort (p, p + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
out (p[i].first);
cout << ' ';
out (p[i].second);
cout << '\n';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> n)
solve();
}
4. /╲/\(•̀w•́)/\╱\ (Zerojudge_f973)
題目:比較此函數在兩點的大小,並輸出斜率。
解法:這個函數叫魏爾施特拉斯函數,是第一個發現的不可微分連續函數。求值大概求前 $5、6$ 項就好了,因為後面的誤差很小。說什麼斜率要四捨五入都是騙人的
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
const LD pi = acos (-1);
LD a, b;
LD f (LD x) {
LD re = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++)
re += pow (a, i) * cos (pow (b, i) * pi * x);
return re;
}
void solve() {
LD x1, x2;
cin >> x1 >> x2;
x1 = f (x1), x2 = f (x2);
if (-1 < x1 - x2 && x1 - x2 < 1)
cout << "Tie\n";
else if (x1 > x2)
cout << "Bully Maguire Wins\nnan\n";
else
cout << "Zemo Wins\nnan\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> a >> b)
solve();
}
5. 我看你…完全是不懂喔 (Zerojudge_f974)
題目:求 $1+x+x^2+x^3+...+x^n \% 1000000007$ 的數。
解法:拆成兩份,然後用快速冪合併。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll mod = 1000000007;
ll x, n;
ll getn (ll num) {
if (num == 0)
return 1;
if (num == 1)
return x;
ll ans = 1, mult = x;
while (num) {
if (num & 1)
ans = ans * mult % mod;
num /= 2;
mult = mult * mult % mod;
}
return ans;
}
ll Sn (ll num) {
if (num == 0)
return 1;
if (num == 1)
return 1 + x;
if (! (num & 1)) {
ll sum = (x + getn (num / 2 + 1)) * Sn (num / 2 - 1) + 1;
sum %= mod;
return sum;
} else {
ll sum = (1 + getn ( (num + 1) / 2)) * Sn ( (num - 1) / 2);
sum %= mod;
return sum;
}
}
void solve() {
cout << Sn (n) << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> x >> n && ! (x == 0 && n == 0))
solve();
}
使用模運算可加速
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 1000000007;
unsigned LL x, n;
int power (int d, LL up) {
if (up == 0)
return 1;
int ans = 1, mult = d;
while (up) {
if (up & 1)
ans = (LL) ans * mult % MOD;
mult = (LL) mult * mult % MOD;
up >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
void solve() {
if (x == 1)
cout << (n % MOD + 1) % MOD << '\n';
else {
cout << (LL) (power (x, n + 1) - 1) *power (x - 1, MOD - 2) % MOD << '\n';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> x >> n && x && n)
solve();
}
6. Loki ✘ Sylvie (Zerojudge_f975)
題目:邊長為 $1$ 的正 $n$ 邊形,各個頂點朝下 $k$ 個頂點前進,速率等於 $1$,求到中點時間。
解法:可挑兩點,算兩點距離,每秒拉近多長,算出時間。見文章。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
const LD pi = acos (-1);
LD n, k;
void solve() {
LD len = sqrt (1 / (2 * (1 - cos (2 * pi / n))));
len *= sqrt (2 * (1 - cos (k * 2 * pi / n)));
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << len / (1 + cos (pi - k * 2 * pi / n)) << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> n >> k)
solve();
}
7. The Adventure of Morty and Jessica (Zerojudge_f976)
題目:$a(v) = a_0-kv$ ( $a_0$ 為常數 ),求 $x(t), v(t), a(t)$。
解法:
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
LD a, k, t;
void solve() {
cout << "x(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << a* (exp (-k * t) + k * t - 1) / (k * k) << '\n';
cout << "v(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << a* (1 - exp (-k * t)) / k << '\n';
cout << "a(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << a*exp (-k * t) << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> a >> k >> t)
solve();
}
8. '97 Bonnie & Clyde (Zerojudge_f977)
題目:$a(v) = a_0-kv^2$ ( $a_0$ 為常數 ),求 $x(t), v(t), a(t)$。
解法:如果 $e$ 的次方數很高,有一些地方就能取近似值。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
LD a, k, t;
const LD ln2 = log (2);
void solve() {
LD num = 2 * sqrt (a * k) * t;
if (num >= 30) {
cout << "x(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << num / k - ln2 / k - sqrt (a / k) *t << '\n';
cout << "v(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << sqrt (a / k) << '\n';
cout << "a(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << "0.00\n";
} else {
LD ex = exp (num);
cout << "x(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << log (ex + 1) / k - ln2 / k - sqrt (a / k) *t << '\n';
cout << "v(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << sqrt (a / k) * (ex - 1) / (ex + 1) << '\n';
cout << "a(" << fixed << setprecision (0) << t << ")=";
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << 4 * a*ex / (ex + 1) / (ex + 1) << '\n';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> a >> k >> t)
solve();
}
9. Ook! (Zerojudge_f978)
題目:模擬 $\text{Ook!}$ 語言 (跟 $\text{BF}$ 很像)。
解法:要判斷有沒有編譯成功,要看幾個地方,像是 $\text{Ook}$ 數量為偶數,不會有 $\text{Ook? Ook?}$ 出現,還有括號要匹配成功。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string order[3] = {"Ook.", "Ook!", "Ook?"};
int type (string s) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
if (s == order[i])
return i;
return -1;
}
void solve() {
string str;
bool ok = 0;
int n, sum = 0;
while (cin >> str) {
if (ok == 0) {
ok = 1;
n = type (str);
if (n == -1) {
cout << "Ook. Ook. Ook! Ook! Ook. Ook.\n";
return;
}
} else {
ok = 0;
n = n * 3 + type (str);
if (n == 8 || type (str) == -1) {
cout << "Ook. Ook. Ook! Ook! Ook. Ook.\n";
return;
}
if (n == 5)
sum++;
else if (n == 7) {
sum--;
if (sum == -1) {
cout << "Ook. Ook. Ook! Ook! Ook. Ook.\n";
return;
}
}
}
}
if (ok == 1 || sum != 0)
cout << "Ook. Ook. Ook! Ook! Ook. Ook.\n";
else
cout << "Ook. Ook? Ook! Ook! Ook? Ook.\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
solve();
}
10. Purple Hills (Zerojudge_f979)
題目:計算 $1+2\times x+...+(n+1)\times x^n$ 的值。
解法:分兩份,把其中一份多餘的先算出來,再合併。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll mod = 1000000007;
ll x, n;
ll getn (ll num) {
if (num == 0)
return 1;
if (num == 1)
return x;
ll ans = 1, mult = x;
while (num) {
if (num & 1)
ans = ans * mult % mod;
num /= 2;
mult = mult * mult % mod;
}
return ans;
}
ll S1 (ll num) {
if (num == 0)
return 1;
if (num == 1)
return 1 + x;
if (! (num & 1)) {
ll sum = (x + getn (num / 2 + 1)) * S1 (num / 2 - 1) + 1;
sum %= mod;
return sum;
} else {
ll sum = (1 + getn ( (num + 1) / 2)) * S1 ( (num - 1) / 2);
sum %= mod;
return sum;
}
}
ll S2 (ll num) {
if (num == 0)
return 1;
if (num == 1)
return 1 + 2 * x;
if (! (num & 1)) {
ll sum = S2 (num - 1) + (num + 1) * getn (num);
sum %= mod;
return sum;
} else {
ll sum, temp;
temp = getn ( (num + 1) / 2);
sum = (num + 1) / 2 * temp % mod * S1 ( (num - 1) / 2) % mod;
sum = (sum + (1 + temp) * S2 ( (num - 1) / 2)) % mod;
return sum;
}
}
void solve() {
cout << S2 (n) << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> x >> n && ! (x == 0 && n == 0))
solve();
}
使用模運算可加速
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 1000000007;
LL x, n;
LL power (LL d, LL up) {
if (up == 0)
return 1;
LL ans = 1, mult = d % MOD;
while (up) {
if (up & 1)
ans = ans * mult % MOD;
mult = mult * mult % MOD;
up >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
void solve() {
if (x == 1) {
cout << (n + 1) * (n + 2) / 2 % MOD << '\n';
return;
}
LL temp = power (x, n + 1), ans;
ans = (n + 1) * temp % MOD;
temp = (temp - 1) * power (x - 1, MOD - 2) % MOD;
ans = (ans + MOD - temp) % MOD;
ans = ans * power (x - 1, MOD - 2) % MOD;
cout << ans << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> x >> n)
solve();
}
11. Without Me (Zerojudge_f980)
題目:算出 $n!\ \text{mod}\ P$ 的值
解法:如果 $n ≥ P$,答案就會是 $0$。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string n, p;
bool cmp() {
if (n.length() != p.length())
return n.length() > p.length();
return n > p;
}
int num (string str) {
int re = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
re = re * 10 + str[i] - '0';
return re;
}
void solve() {
if (cmp()) {
cout << "0\n";
} else {
int ans = 1, N = num (n), P = num (p);
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
ans = ans * i % P;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> n >> p)
solve();
}
12. P = NP (Zerojudge_f981)
題目:求出 $Ax^2+Bx+C=0$ 的根 ($A, B, C$ 為複數)。
解法:可使用 $\text{complex}$ 函式庫。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
complex<LD> A, B, C;
LD a1, a2, a3, b1, b2, b3;
complex<LD> cpx (LD a, LD b) {
complex<LD> re = {a, b};
return re;
}
void out (LD x, bool pref) {
if (-0.005 < x && x <= 0) {
cout << (pref == 1 ? "+0.00" : "0.00");
return;
}
if (x < 0)
cout << '-', x = -x;
else if (pref == 1)
cout << '+';
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << x;
}
bool iszero (complex<LD> x) {
bool zero1 = 0, zero2 = 0;
if (-1e-10 < x.real() && x.real() < 1e-10)
zero1 = 1;
if (-1e-10 < x.imag() && x.imag() < 1e-10)
zero2 = 1;
return (zero1 && zero2);
}
void solve() {
A = {a1, b1};
B = {a2, b2};
C = {a3, b3};
complex<LD> d = B * B - cpx (4, 0) * A * C;
if (iszero (d)) {
d = -B / (cpx (2, 0) * A);
cout << "the only x = ";
out (d.real(), 0);
out (d.imag(), 1);
cout << "i\n";
} else {
complex<LD> ans1, ans2;
ans1 = (-B + sqrt (d)) / (cpx (2, 0) * A);
ans2 = (-B - sqrt (d)) / (cpx (2, 0) * A);
if (ans1.real() > ans2.real() || (ans1.real() == ans2.real() && ans1.imag() > ans2.imag())) {
complex<LD> temp = ans1;
ans1 = ans2;
ans2 = temp;
}
cout << "first x = ";
out (ans1.real(), 0);
out (ans1.imag(), 1);
cout << "i, second x = ";
out (ans2.real(), 0);
out (ans2.imag(), 1);
cout << "i\n";
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> a1 >> b1 >> a2 >> b2 >> a3 >> b3)
solve();
}
13. Gary 和 Eric 撞來撞去 (Zerojudge_f982)
題目:給 $m_1$ 和 $m_2$,求在完全彈性碰撞下的碰撞次數。
解法:答案為 $atan(π/\sqrt{m1/m2})$。見 Youtube。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
const LD pi = acos (-1);
LD m1, m2;
void solve() {
cout << (long long) (pi / atan (sqrt (m1 / m2))) << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> m1 >> m2)
solve();
}
14. Ginobesity (Zerojudge_f983)
題目:$D(x,y,z)=f(x)+g(y)+h(z)$,求 $(0,0,0)$ 到 $(n,m,k)$ 的總重量。
解法:令 $F'(x)=f(x)$,$G'(y)=g(y)$,$H'(z)=h(z)$,則答案為 $m\times k\times (F(n)-F(0))+n\times k\times (G(m)-G(0))+n\times m\times (H(k)-H(0))$。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
int n[3];
void solve() {
LD ans = 0;
int a[3];
cin >> a[0] >> a[1] >> a[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
LD sum = 0, num;
a[i]++;
while (a[i]) {
cin >> num;
sum = (sum + (LD) num / a[i]) * n[i];
a[i]--;
}
ans += n[0] * n[1] * n[2] / n[i] * sum;
}
if (-0.005 < ans && ans <= 0) {
cout << "0.00\n";
return;
}
if (ans < 0)
cout << '-', ans = -ans;
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << ans << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> n[0] >> n[1] >> n[2])
solve();
}
15. 蠑螈 (Zerojudge_f984)
題目:給座標,用迴歸平面求 $z$ 座標。
解法:見文章。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
int n;
LD av[3], num[3][105];
LD multsum[3][3];
LD r[3][3], o[3];
LD a, b;
void init() {
cin >> n;
av[0] = av[1] = av[2] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
cin >> num[j][i], av[j] += num[j][i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < 3; j++) {
multsum[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
multsum[i][j] += num[i][k] * num[j][k];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
av[i] /= n;
o[i] = sqrt ( (multsum[i][i] - n * av[i] * av[i]) / (n - 1));
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < 3; j++) {
r[i][j] = (multsum[i][j] - n * av[i] * av[j]) / (o[i] * o[j]);
}
}
a = r[0][2] * (r[1][2] - r[1][1]) / (2 * (r[0][0] * r[1][1] - r[0][1] * r[0][1]));
b = (r[0][1] * r[0][2] - r[0][0] * r[1][2]) / (2 * (r[0][0] * r[1][1] - r[0][1] * r[0][1]));
}
void out (LD k) {
if (-0.005 < k && k <= 0) {
cout << "0.00\n";
return;
}
if (k < 0)
k = -k, cout << '-';
cout << fixed << setprecision (2) << k << '\n';
}
void solve() {
init();
int q;
cin >> q;
while (q--) {
LD x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
out (a * o[2] * (x - av[0]) / o[0] + b * o[2] * (y - av[1]) / o[1] + av[2]);
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
}
16. 攗皥蒽快給我去工作!!!(Zerojudge_f985)
題目:$A\times B=C$,給你 $A, C$,求出 $B$。
解題:求 $A$ 的反矩陣 $A'$,$B=A'AB=A'C$。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#define LD long double
using namespace std;
struct mat {
LD num[3][3], det;
void init() {
det = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
cin >> num[i][j];
det += num[0][0] * num[1][1] * num[2][2];
det += num[0][1] * num[1][2] * num[2][0];
det += num[0][2] * num[1][0] * num[2][1];
det -= num[0][2] * num[1][1] * num[2][0];
det -= num[0][1] * num[1][0] * num[2][2];
det -= num[0][0] * num[1][2] * num[2][1];
}
};
string str;
mat A, B, C;
void change_num() {
mat temp = A;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
LD arr[2][2];
int xnow = 0, ynow = 0;
for (int ii = 0; ii < 3; ii++) {
if (ii == i)
continue;
for (int jj = 0; jj < 3; jj++) {
if (jj == j)
continue;
arr[xnow][ynow] = temp.num[ii][jj];
ynow++;
}
xnow++, ynow = 0;
}
A.num[i][j] = arr[0][0] * arr[1][1] - arr[0][1] * arr[1][0];
if ( (i + j) % 2 == 1)
A.num[i][j] = -A.num[i][j];
}
}
}
void turn() {
mat temp = A;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
A.num[i][j] = temp.num[j][i];
}
void mult() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
B.num[i][j] = (A.num[i][0] * C.num[0][j] + A.num[i][1] * C.num[1][j] + A.num[i][2] * C.num[2][j]) / A.det;
}
void out (LD x) {
if (-0.00005 < x && x <= 0) {
cout << "0.0000";
return;
}
if (x < 0)
cout << '-', x = -x;
cout << fixed << setprecision (4) << x;
}
void outb() {
cout << "B:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
out (B.num[i][j]), cout << (j == 2 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
void solve() {
A.init();
cin >> str;
C.init();
change_num();
turn();
mult();
outb();
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio (false), cin.tie (0);
while (cin >> str)
solve();
}
[離場] (Zerojudge_f033 不公開)
題目:輸出一個可以 $\text{AC}$ 的東西。
解法:輸出答案。
#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "答案\n";
}
我的分享就到這裡結束了,如果喜歡我的 $\text{Blog}$,歡迎追蹤!
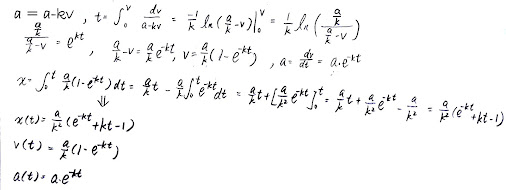

好扯 都用數學電人
回覆刪除